Factors Affecting Overseas Direct Purchase Behavior of Dietary Supplements: Analyzing Korean Internet Articles
Abstract
This research aims to explore the factors influencing Korean consumers' decisions to purchase dietary supplements from overseas markets. It seeks to identify the potential impacts that the increased trend of overseas direct purchasing, driven by online accessibility and government support, could have on consumers purchasing dietary supplements for a healthy lifestyle. The study analyzes consumer behavior factors related to overseas direct purchases within the consumer domain that prioritizes a healthy lifestyle, providing various implications for dietary supplements and their procurement channels in the sports domain.
The study collected and analyzed a corpus of Korean internet articles from June 7, 2012, to October 8, 2023, focusing on dietary supplement overseas direct purchases. Using the R program, it employed phi-coefficients and bi-gram network word pairs to categorize keywords and explore factors influencing Korean online consumer purchase behavior from overseas.
The analysis identified environmental influences and product/service characteristics as pivotal factors influencing these purchasing decisions. It revealed a significant trend towards a health-conscious lifestyle among Korean consumers, driving them towards overseas direct purchases of dietary supplements. In addition, in accordance with the characteristics of news articles, side effects caused by the consumption of supplements purchased through overseas direct buying and warnings about illegal secondary markets have also been identified.
The findings offer significant insights into the complex cross-border purchasing behavior of dietary supplement consumers, closely linked to a health-conscious lifestyle. These insights have implications for marketing strategies, supplement regulatory frameworks, and educational initiatives within the sports sector, emphasizing the importance of understanding consumer behavior in the context of overseas direct purchases.
Keywords:
Dietary supplements, Overseas direct purchase, Purchase behavior, Korean consumers, Health-conscious lifestyle, Online marketIntroduction
In accordance with data derived from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), a comprehensive nationwide initiative mandated by the National Health Promotion Act to assess the health statuses, behaviors, and dietary patterns of the South Korean population, there has been a consistent upward trajectory in the prevalence of dietary supplement consumption. The most recent statistics available from the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA), pertaining to the 2022 iteration of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, reveal that the prevalence of dietary supplement usage escalated to 69.1% among the adult demographic in 2021.This trend is not limited to Korea, but is similarly seen in the United States and Europe (Dickinson & Mackey, 2014; Kofoed et al, 2015). This reflects the global movement toward health and wellness. As the population pursues a healthier lifestyle, interest in and consumption of dietary supplements has increased. While the production and sales of dietary supplements by domestic companies have increased, the number of Korean consumers who purchase dietary supplements through online markets has also increased as overseas consumers have become easier (Kim et al, 2018; Choi, 2017). The surge in overseas direct purchases, especially in the U.S., is attributed to the increasing number of consumers looking for cost-effective and effective supplements. Data from the Korea Customs Service showing that overseas direct purchases reached a record high of 96 million cases in 2022, valued at $47.25 million, underscores the role of the internet in changing the purchasing pathways and habits of domestic consumers. Despite the presence of certified dietary supplements in the country, the ease with which dietary supplements from overseas with different regulations can be brought into the country has created a need for navigation.
According to the 'E-Nation Indicator' offering statistical insights into Korea, the global supplement market in 2020 reached approximately $158.2 billion. The United States led with 35.2%, followed by China at 14.3%, and Western Europe at 12.0%. South Korea, along with Taiwan and Indonesia, constituted the 'Other Asia' category, holding a 10.9% share of the supplement industry in 2020. This international perspective highlights Korea's susceptibility to influence, particularly by the U.S. market, especially evident in overseas direct purchases.
In accordance with the amendments made on February 3, 2015, to South Korean Health functional food regulations, the term "Health Functional Food" pertains to food items manufactured and processed using raw materials or ingredients possessing functional properties beneficial to the human body (Health Functional Food Act 3.1, 2021). The use of the words "health functional food" or the designated design serves as an indicator of its status as a health functional food (Health Functional Food Labeling Standards 6.1, 2023). The Korea Food and Drug Administration (KFDA) administers the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for Health Functional Foods Standards (2022) to regulate the manufacturing and quality control of high-quality health functional foods. As above, dietary supplements that meet the regulations are referred to as "Health Functional Food" and are managed and regulated in Korea. In the case of dietary supplements through overseas direct sales, it should be noted that each country has different regulations and management of dietary supplement manufacturing. As more individuals buy directly from overseas online markets, it can be difficult to keep track of the many products that come directly from overseas.
The challenge in discussing dietary supplement regulation stems from the absence of a global consensus on defining products categorized differently across countries, such as dietary supplements, natural health products (NHP), complementary medicines, or food supplements. Therefore, side effects or complications of consumers who directly purchase dietary supplements abroad for a healthy lifestyle cannot be overlooked. Themed articles object to the overall cases associated with directly purchasing dietary supplements not officially imported domestically. Research on dietary supplements has been ongoing, especially in sports, where the use of dietary supplements is widespread (Hoyte et al., 2013; Kim et al., 2008; Lee, 2006; Knapik et al., 2021; Nam & Cho, 2019; Lee & Kang, 2019), and research on specific supplement purchase pathways is also of interest in the field of sports. Most sports supplement research also focuses on side effects and safety (Nam & Cho, 2019; Andres et al, 2017; Lee & Kang, 2019; Hoyte et al, 2013).
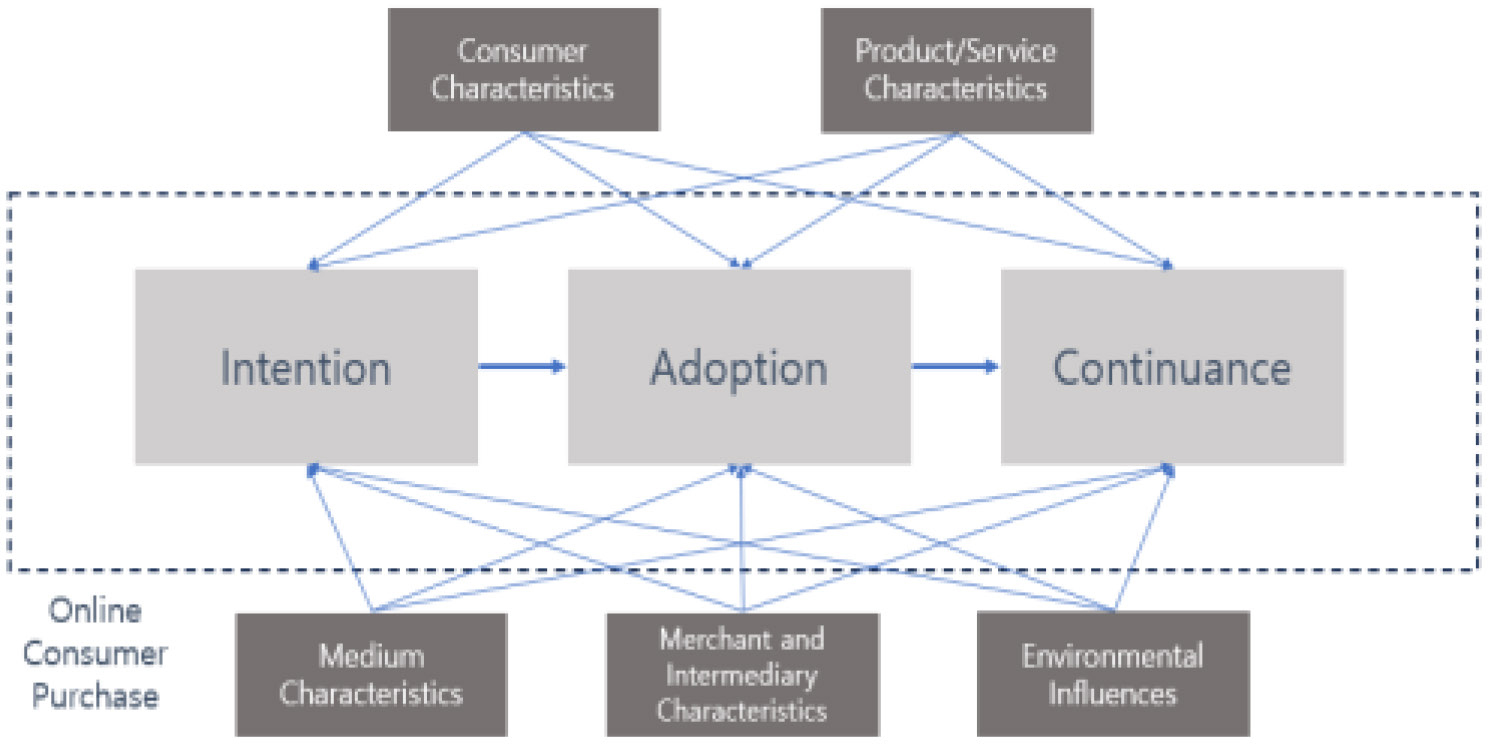
Consumer purchasing behavior has evolved from the traditional model of direct transactions to online interactions and purchases, highlighting the expansion of the online market. The prevalence of overseas direct purchasing serves as evidence for this digital market growth. The traditional five-stage decision model has been instrumental in reevaluating decision-making models for modern consumers (Comegys et al., 2006). Stankevich (2017) underscores the importance of adapting to dynamic consumer trends. The active engagement of domestic consumers in overseas direct purchasing since the 2010s can be attributed to the development of e-commerce facilitated by advancements in the internet and translation tools. The significance of conducting research that distinguishes itself from traditional consumer behavior has been affirmed by various previous studies (Pappas, 2016; Stankevich, 2017; Zhou et al., 2007; Marton & Wei Choo, 2012). Cheung et al. (2005) pointed out that research on online consumer theory is diverse but lacks a unified theoretical foundation due to its wide scope, and proposed a model consisting of five factors that complexly influence the transition from intention to adoption and persistence of online consumer purchase behavior.
Drawing from previous research and acknowledging the global expansion of the online market, this study used an existing integrated conceptual model to comprehend the purchasing behavior of domestic consumers participating in overseas direct purchases of dietary supplements, which comprehensive model in the work of Cheung et al. (2005) framework. Each factor of determinants of online consumer behavior provides a consistent perspective explicitly designed for the research cohort, focusing on domestic consumers engaged in overseas direct purchases of dietary supplements. Based on the presented antecedent model, the main objective of this study is to examine each of the five factors that influence domestic consumers' decisions to engage in overseas direct purchases of dietary supplements. In particular, we analyze Internet articles related to this trend in the context of health-conscious lifestyles and sports to understand the implications for consumers purchasing dietary supplements.
Methods
Data collection
In conducting this study, we leveraged news data from online media outlets, utilizing the analysis system provided by Bigkinds (www.bigkinds.or.kr), a platform under the Korea Press Foundation. Our search focused on news data related to 'dietary supplements' and 'overseas direct purchases.' To ensure the credibility of the information, we followed the Korea Press Foundation's guidelines, and excluded certain specialty newspaper articles whose credibility has come under scrutiny, often characterized by a focus on clickbait rather than consistent quality. The study encompassed a dataset of 910 articles, spanning from June 7, 2012, the inception of relevant internet articles, to October 8, 2023, when it finished collecting them for data analysis. The starting date of June 7, 2012, marks the publication of the first internet article addressing overseas direct purchasing and dietary supplements, which began gaining traction of the 2010s. This overall timeframe was chosen to facilitate a comprehensive examination of the evolving landscape surrounding supplements and direct sales within the Korean context.
To comprehensively gather data related to supplements and direct sales, meticulously crafted a search formula incorporating commonly used terms in the Korean context. The formula employed was "(보충제 OR 영양제 OR 스포츠보충제 OR 건강기능식품 OR 건기식 OR 식이보충제 OR 스포츠영양제) AND (해외직구 OR 해외직접구매)" These terms were meticulously targeted within both the title and body of the news articles. Notably, the terms "해외유통" and "직구" were deliberately excluded from the search formula. This decision was driven by their high search frequency and perceived neutrality as expressions. The term "직구" is often used in conjunction with "해외직구," and "해외유통" was omitted due to its broader scope, encompassing distribution-related content beyond direct purchases.
In our pursuit of exhaustive results, we implemented a sophisticated morpheme/bigram analysis. This approach aimed to enhance search precision, leaving no room for oversight and guaranteeing a comprehensive compilation of relevant articles. A total of 793 article texts were analyzed as the final data after refining duplicate and irrelevant articles to identify the factors that influence overseas direct purchase among dietary supplement buyers in accordance with the study objectives.
R text-mining
The R programming language was used to analyze the body text of the collected articles. The 'KoNLP' package was used for Korean language analysis, and the 'dplyr' and 'tidyr' packages were used for text preprocessing. The refined dataset underwent morphological analysis to segment it into nouns, verbs, and adjectives. Words with more than two letters were retained for analysis to ensure the relevance of the extracted terms. Additionally, verbs and adjectives, apart from nouns, were also extracted, acknowledging that the meaning of nouns can vary based on the associated verb or adjective (Kim, 2021). As with the previous collection of articles, similar synonyms were also unified to solve the problem of ambiguity in the network structure between texts due to various similar words for 'overseas direct purchase'. It is noteworthy that, throughout this process, the inclusion of keyword data is retained intentionally, with the deliberate decision to abstain from its removal. This strategic choice is made to preserve the integrity of the network structure, as removing keyword data could potentially result in alterations to the overall network configuration. This strategic choice is made to preserve the integrity of the network structure, as removing keyword data could potentially result in alterations to the overall network configuration.
A multi-method approach, two analysis methods were used together to improve reliability. Text mining in R presents the advantage of intuitively analyzing texts, although it is accompanied by the challenge of determining confidence levels. To address this limitation, two distinct network analysis methods were utilized to examine the relationship between crucial words. The utilization of both pie coefficient and bi-gram analysis methods, along with a thorough examination of the results, aimed to enhance the reliability of the analysis by cross-verifying and validating overlapping or similar outcomes.
Classification
The categorization process followed the 5 factors that mentioned in Cheung et al. (2005) framework of online consumer behavior. The identified keyword pairs within these clusters were systematically classified according to the five factors influencing online consumer purchase behavior as phi-correlation and bi-gram analysis. The descriptions, key constructs, and examples provided by Cheung et al (2005). The criteria for classifying keyword pairs according to the five purchase factors. First, a direct classification based on keyword pairs was conducted. The pairing of two words made it possible to classify the factors of word pairs, and when the classification of factors was difficult or ambiguous, the network structure was examined to identify and classify related surrounding words. If the factor classification remained inconclusive even after examining the network structure, the pairs were excluded from the classification process.
Results
Phi-coefficient analysis
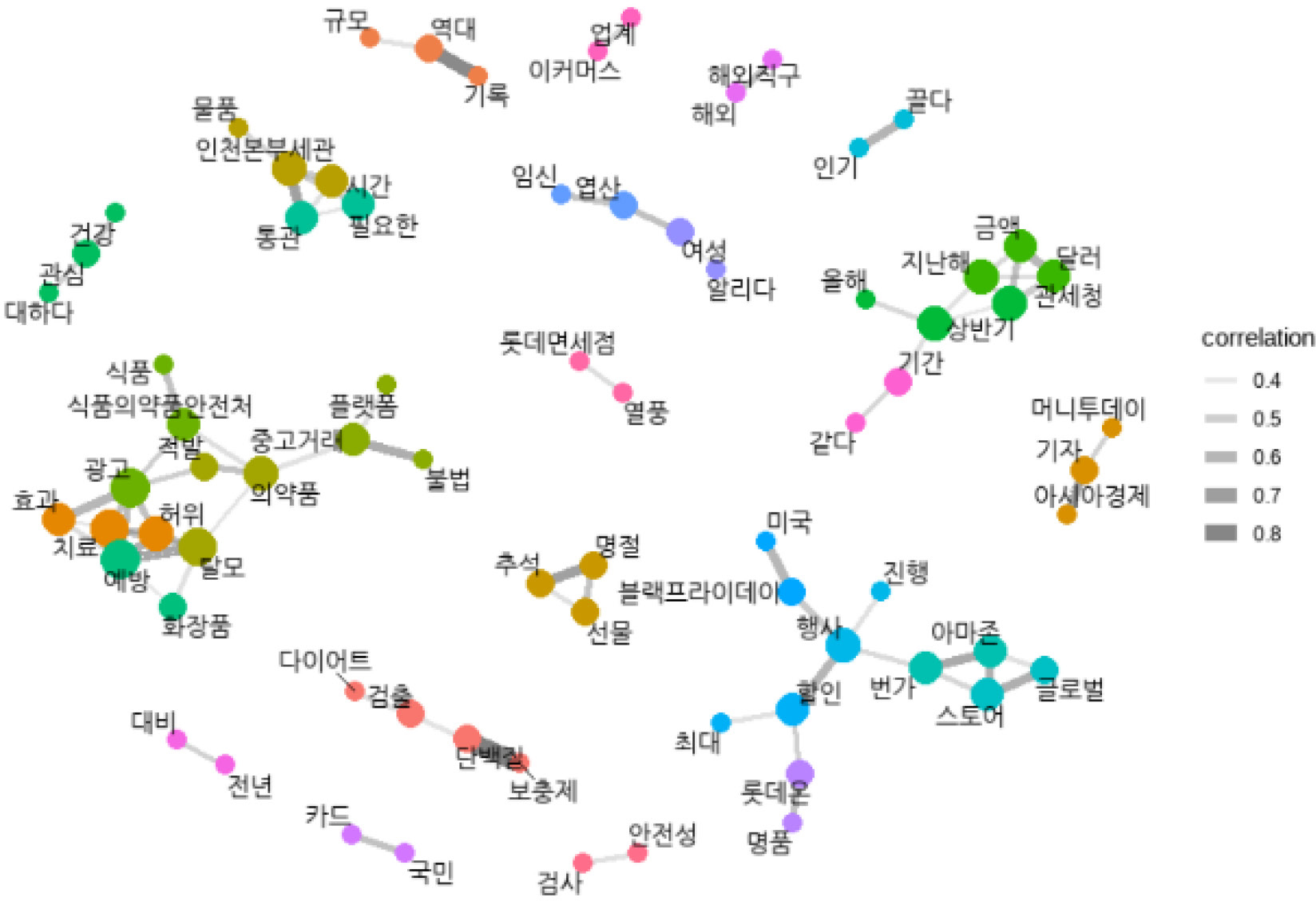
8764 pairs of keywords with positive phi coefficients were identified. Words with low significance were excluded, refining the dataset.
The subsequent step involved the identification of network clusters. Word pairs with a correlation greater than or equal to 0.35 (a total of 76 word pairs) were used to delineate a more accurate network structure.
Bi-gram analysis
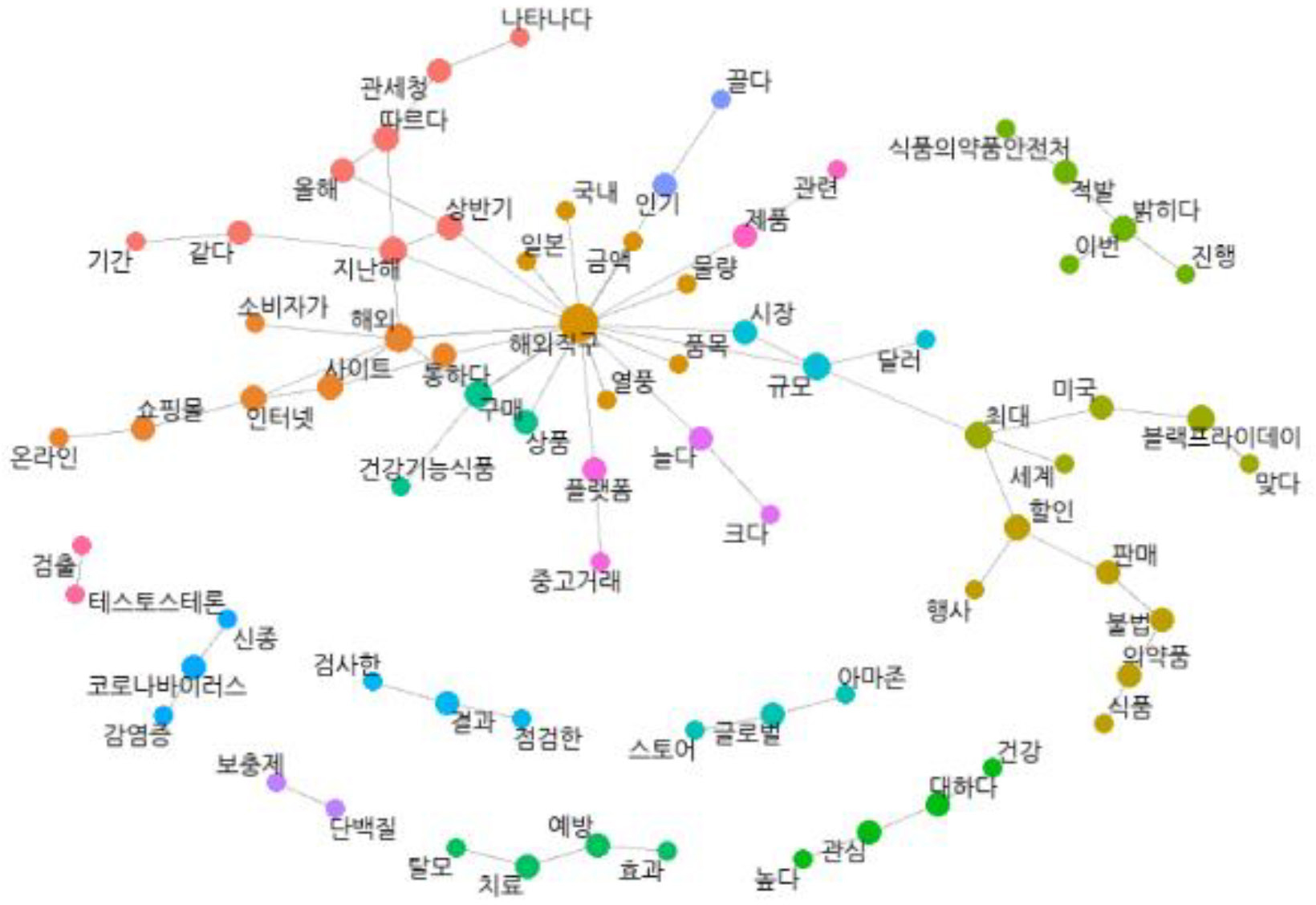
The utilization of word pairs derived from the phi coefficient primarily emphasizes the co-occurrence of words, posing challenges in deciphering the contextual meaning when words are interconnected. To address this limitation, a parallel analysis using the bi-gram network was conducted. Bi-gram analysis allows for the identification of two consecutive words, shedding light on the semantic relationship between keywords.
The bi-gram analysis yielded a total of 18,401 consecutive word pairs. For a more accurate network structure, word pairs with a frequency (N) were greater than or equal to twelve, resulting in a total of 76 clusters.
The phi-correlation analysis resulted in a relatively low classification of keyword pairs, but there were some notable keyword pairs. Since there are no keywords categorized under this factor in the bi-gram analysis, we can say that it has a relatively low impact in this study compared to other factors.
Within the realm of women's health, several articles have surfaced detailing the illicit shipment of abortifacients, categorized as specialty drugs and prohibited for sale in Korea (Bae, 2019; Cha, 2019). Highlighting the variations in drug classifications across nations, Bae (2019) emphasized the need for consumers to exercise extreme caution when procuring illicit products containing the abortifacient known as "mifzin" or the performance-enhancing drug Stanozolol.
The consumer attributes of '여성(women)’ and '임신(pregnancy)’ demonstrated a robust association with the keyword 'folic acid.' The news articles highlighted the significance of folic acid as a crucial nutrient for women in early pregnancy, underscoring the importance of choosing natural folic acid over synthetic forms (Kwak, 2016; Byun, 2016). These findings underscore the intimate connection between folic acid (vitamin B9) and the consumer characteristic of pregnancy. The purchasing method was also mentioned. According to Jung's news article (2015), the domestic market for folic acid supplements continues to expand. Many consumers prefer to procure recommended products from well-known brands such as 나우푸드, GNC, and 암웨이 through international direct purchase platforms like iHerb and Amazon (para. 3). The article highlights that only a few among the myriad of folic acid products on the market are free from chemical additives, necessitating careful product selection.
The second most important in this study was attributed to product/service characteristics, categorizing them as a significant factor. These characteristics are deemed crucial in understanding consumer behavior. Noteworthy keywords related to product attributes include 'protein' and 'hair loss.' Particularly, the pi correlation coefficient for 'protein' exceeds 0.8, underscoring its strong association with dietary supplements. Additionally, the appearance of keyword pairs involving 'hair loss' in both the pi coefficient and bi-gram analyses suggests the widespread use of supplements for addressing hair loss concerns. Within the category of product/service characteristics, negative terms such as '허위(false)', '검출(detection)', and '테스토스테론(testosterone)' emerge. Specifically, word pairs like '검출-다이어트(detection-diet)', '검출-단백질(detection-protein)', and '테스토스테론-검출(testosterone-detection) ' are identified as pivotal concerns reflecting the extensive usage of dietary supplements.
Upon examining articles containing the term 'detection-diet,' it was revealed that a considerable number of harmful substances were found in dietary supplements readily available on overseas internet sites, which claim efficacy in improving diet and sexual function (Lee, 2018). Kim (2018) highlighted the detection of 'narcotics' and 'animal drugs' in one out of every five products sold on overseas online sites. Both articles reported inspections conducted in early 2018 on 1,155 dietary supplements available from overseas sites, revealing that 205 products (18.2%) contained substances unfit for food use. Furthermore, in July 2020, an investigation ensued after cassia powder, a dietary supplement sold directly from overseas, was discovered to contain 24 times the standard amount of iron powder (Jo, 2020; Kim, 2020; Yang, 2020).
The co-occurring word pairs 'detection - protein' and 'testosterone - detection' can analyzed together. These pairings are found in articles detailing the identification of testosterone, a steroid, in protein supplements accessible through international direct purchase (Lee, 2019; Lee, 2019; Jung, 2019; Jang, 2019). In 2019, a solitary supplement with such concerns was identified on Amazon, a platform catering to the convenient procurement of products by online consumers. After the inspection, customs authorities formally petitioned for a customs blockade. However, it is imperative to acknowledge the possibility that such products can consistently appear and the inherent temporal constraints associated with regulatory inspections. Further, it is crucial to recognize that the potential risks involved may be of heightened concern, particularly within the demographic of sports participants.
The findings regarding medium characteristics yielded results that were not particularly remarkable. According to the criteria set forth by Cheung et al. (2005), outlining the classification elements, medium characteristics are expected to align with either traditional information systems or web-specific factors. However, upon the categorization of medium characteristics through pie coefficient and bi-gram analyses, it does not appear to emerge as a pivotal factor.
In the factor of merchant and intermediary characteristics, Amazon stands out as a prominent global retailer, evident in both pie coefficient and bi-gram analyses. It is analyzed as a preeminent online store functioning as a dropshipping platform. Despite the relatively limited number of keyword pairs in this factor, the co-occurrence of the terms 'secondary market-platform' and 'illegal' with 'second-hand trade' emerges as a significant keyword pair warranting scrutiny. An examination of articles related to second-hand trading reveals that instances of illegal sales and advertisements of medications on four online non-face-to-face second-hand trading platforms in Korea predominantly involve unlicensed medicines distributed in Korea through overseas direct sales or purchase agencies (Wang, 2023; Park, 2023; Kim, 2023).
It is noteworthy that there are instances where products classified as dietary supplements abroad are treated as medicines in Korea. In the year of this study, November 28, 2023, 'Theobromine,' recognized as a dietary supplement in the United States, was designated by the MFDS to be blocked from import into Korea because it serves as an ingredient in specialized medicines in Korea (Kim, 2023). Additionally, the products targeting muscle building and weight loss, identified as ingredients blocked from import into Korea, prompted the KFDA to implement measures and provide relevant data on the 'Overseas Direct Foods ALL' website.
Furthermore, brands classified under merchant and intermediary characteristics can be discussed in terms of promoting intermediary brands, encompassing credit cards, luxury goods, discounts, and events that have contributed to the proliferation of overseas direct delivery.
The largest number of keyword pairs in this study was attributed to environmental influences, categorizing them as a significant factor in both methods. This factor encompassed consumer culture (Black Friday, Chuseok, festivals, gifts), social issues (COVID-19), and key organizations (Korea Customs Service, Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Incheon Headquarters Customs) etc. Black Friday, an iconic American discount day, has evolved into a prime opportunity for Korean consumers to acquire overseas products at discounted prices. Likewise, Chuseok, one of Korea's major holidays, has become a popular time for purchasing gifts, including dietary supplements, through overseas channels.
The keyword pairs identified shed light on the burgeoning prevalence of the direct-to-consumer culture. Examples include statements such as “해외 직접구매(직구)가 인기를 끌면서 직구 금액이 지난해 사상 처음으로 20억달러를 돌파했다 해외 직접구매(직구)가 인기를 끌면서 직구 금액이 지난해 사상 처음으로 20억달러를 돌파했다” (Kim, 2018) and “해외직구가 인기를 끌면서 관련 라이브커머스 방송도 흥행을 거두고 있다” (Kim, 2021). These positions direct overseas purchases as a noteworthy trend in consumer culture.
Given the nature of the news articles, keyword pairs like 'largest-scale,' 'historical-scale,' and 'record-historical' are discerned, suggesting that overseas job hunting itself is consistently presented as a prominent trend within consumer culture.
Additionally, the pi coefficient and bi-gram analysis revealed analogous keyword pairs, leading to the overarching inference of a pronounced interest in health. According to Kim (2022), in the news article “코로나19 이후 건강식품에 대한 관심이 높아짐에 따라 건강식품 전문관을 신설” (para. 1), a sentiment echoed in other reporters article, where Kim (2022) observed that “건강 관리에 대한 관심이 높아지면서 유명한 건강기능식품을 합리적으로 구매하려는 이들이 늘고 있는 것으로 보인다” (para. 2). Similarly, Kim (2022) remarked that “코로나19 시기를 거치며 개인 면역력 관리와 건강한 삶에 대한 관심이 높아지면서 규모를 키우고 있는 모습이다” (para. 1). Exemplary sentences extracted from these articles vividly illustrate the escalating emphasis on health.
Discussion
The phi-coefficient and bi-gram analyses consistently underscore the pivotal role of Environmental Influences and Product/Service characteristics in shaping purchasing decisions, substantiated by their noteworthy percentages. Specifically, the Environmental Influences factor extends its influence beyond traditional aspects, encompassing consumer culture, social issues, and key organizations. These contributions offer rich contextual insights, enhancing the depth of understanding within the study.
The Product/Service characteristics factor reveals prevalent protein keywords, signifying their prominence as representative dietary supplements. Noteworthy is the observation that individuals seeking hair loss supplements are prevalent, suggesting a potential consideration for professional athletes. Extracted keywords from articles discussing the controversy surrounding testosterone detection in offshore supplements serve as a cautionary note for athletes. Additionally, keywords related to side effects are of significant concern.
Despite a lower keyword count, Consumer Characteristics, particularly for pregnant women, emerge prominently. In addition, the network structures within the other three factors (Product/Service characteristics, Merchant and Intermediary characteristics, and Environmental Influences) highlight interconnectedness among key elements. The composite core of factors accentuates the nuanced dynamics within each characteristic, exemplified by the strong correlation between supplement and protein keywords.
The Merchant and Intermediary characteristics factor brings attention to potential issues in the trade of dietary supplements through secondary markets. This is evident in keyword pairs such as 'secondary market-platform' and 'illegal secondary market’.
This study has a number of practical implications, ranging from dietary supplement buyers who favor healthy lifestyles to specific target audiences. First, exploring international direct-to-consumer pathways and dietary supplements can reveal opportunities for marketing strategies. Companies can also tailor their messaging and product offerings to evolving consumer preferences, emphasizing the nutritional aspects that resonate most with their target audiences. Additionally, the interconnected network structures identified across the various elements can provide insights for marketers to develop holistic campaigns. They can also position their products in the broader context of consumer preferences and environmental impacts, allowing for an approach that takes into account the multifaceted nature of consumer decision-making. Secondly, it can be used as an educational resource among athletes who need to be sensitive to dietary supplements. Awareness can be raised among athletes about the potential risks and controversies surrounding certain supplements, such as the detection of testosterone in overseas products. Athletes' own knowledge and awareness can play an important role in protecting themselves from dietary supplements and staying safe as an athlete. Finally, various regulations and policies can be put in place. Given the challenges of testing and regulating dietary supplements in international markets, practical collaboration between regulators, sports organizations, industry stakeholders, and others can be beneficial. This would ensure safety and integrity for different ages and genders, and for specific professions such as athletes. It would include developing strong regulations and policies that address the challenges posed by cross-border purchases.
The theoretical implications of this study extend beyond the immediate context of cross-border acquisition of dietary supplements and delve into broader areas of consumer behavior, marketing, and cultural considerations. The findings underscore the intricate dynamics between Product/Service characteristics, Merchant and Intermediary characteristics, and Environmental Influences. This intricate interplay suggests the need for a more nuanced theoretical framework that integrates these factors comprehensively, acknowledging the interconnectedness among them. The network structures identified within the factors hint at the complexity of relationships among key elements. The theoretical implications lie in the exploration of network theory and its application to consumer behavior analysis. Understanding how these networks influence decision-making processes can contribute to the development of more robust theoretical models for studying consumer choices in the overseas direct purchase marketplace.
In an effort to enhance the reliability of the study results, both phi-coefficient and bi-gram analyses were utilized to analyze factors. However, the limitation of this study is the relatively small dataset used to analyze the purchase behavior factors trends in overseas direct purchasing and dietary supplements, a topic that has been active since the 2010s. Over the 12-year period from which the data was collected, the dataset comprised 793 articles, which is insufficient for a meaningful trend analysis when split into smaller time segments. Future research could yield deeper insights related to overseas direct purchases of dietary supplements if a larger dataset is gathered over a sufficient period.
Conclusion
In the context of the globalized era, the landscape of Korean overseas direct purchases has undergone a transformative shift, particularly in the domain of health foods and dietary supplements. Termed 'Overseas Direct Purchases (해외직구),' this trend has been seamlessly integrated into daily life since 2010, riding the wave of increased internet usage and the widespread adoption of smartphones and tablets. The surge in personal overseas shopping is emblematic of a tech-savvy consumer base seeking cost-effective alternatives, leading to an increase in direct imports through online platforms and direct transactions with international sellers. The emergence of the term "Jikgu-zok (직구족)" reflects the identity of those actively participating in these direct overseas purchases. The dynamic evolution of Korean overseas direct purchases reflects a complex interplay of global cultural trends, economic considerations, and health-conscious consumer behaviors. As this industry continues its robust growth, addressing the challenges and risks inherent in direct international purchases, particularly in the dietary supplements realm, emerges as a critical imperative necessitating attention and education.
In this study, the most significant factor influencing the purchase of dietary supplements among Korean consumers is 'environmental factors'. 'Product/service characteristics' are also analyzed as a major factor. As the demand for a healthy lifestyle increases, the investigation into the key purchase channels for dietary supplements distinguishes this study from traditional research. Considering the rising trend of overseas direct purchases among Korean consumers, this research is particularly important within the sports consumer domain.
In conclusion, the intertwining forces of global accessibility, cultural shifts, and consumer consciousness have propelled Korean consumers into a new era of overseas direct purchases, shaping their choices and preferences in health-related domains. As this phenomenon continues to gain momentum, understanding and navigating the intricacies of dietary supplement purchases in the international arena emerge as crucial aspects for both consumers and stakeholders. This study not only sheds light on the prevailing patterns and factors but also lays the foundation for informed decision-making, marketing strategy, education, and policy formulation within the ever-evolving landscape of overseas direct purchases in Korea.
The domestic internet articles utilized as research data for this study numbered less than a thousand for approximately ten years. Expanding the dataset in future research could allow for critical supplementary investigations based on temporal considerations. The choice to utilize news data rather than surveys may facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the overall context over the past decade, but inherent material limitations may hinder the precise identification of various purchasing factors. In terms of analysis, future studies could derive more meaningful results by focusing on specific objectives related to identifying purchase behavior factors in the context of overseas direct purchases of dietary supplements. Additionally, it is recommended that future research builds upon this study, focusing more specifically on diverse levels of sports participants engaged in overseas supplement buying. Dietary supplements play a crucial role, particularly for people who want a healthy lifestyle, and analyzing their consumption behavior and factors could prove beneficial across various facets of the sports industry. Furthermore, as this study presents the first exploration into overseas direct procurement of dietary supplements in Korea, it provides comprehensive factor-based information and network structures but does not delve into specific targets or objectives. Subsequent research endeavors could leverage this study across diverse purposes, such as marketing, regulations, policies, and sports nutrition.
References
-
Andres, S., Ziegenhagen, R., Trefflich, I., Pevny, S., Schultrich, K., Braun, H., . . . Lampen, A. (2017). Creatine and creatine forms intended for sports nutrition. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 61(6), 1600772-N/a.
[https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201600772]
- Bit-na Kim. (2021, June 5). Making $35 Million in Sales through Live Commerce for Overseas Direct Purchases. The Korea Herald. http://biz.heraldcorp.com/view.php?ud=20210604000825
-
Blendon, R. J., DesRoches, C. M., Benson, J. M., Brodie, M., & Altman, D. E. (2001). Americans' views on the use and regulation of dietary supplements. Archives of internal medicine, 161(6), 805-810.
[https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.161.6.805]
-
Cheung, C. M., Chan, G. W., & Limayem, M. (2005). A critical review of online consumer behavior: Empirical research. Journal of electronic commerce in organizations (JECO), 3(4), 1-19.
[https://doi.org/10.4018/jeco.2005100101]
- Choi, S. Y. (2017). An analysis on effective factors of functional food purchase intention applying an extended model of goal-directed behavior (Doctoral dissertation, The Graduate School Ewha Womans University).
-
Comegys, C., Hannula, M., & Väisänen, J. (2006). Longitudinal comparison of Finnish and US online shopping behaviour among university students: The five-stage buying decision process. Journal of Targeting, Measurement and Analysis for Marketing, 14, 336-356.
[https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jt.5740193]
-
Dickinson, A., & MacKay, D. (2014). Health habits and other characteristics of dietary supplement users: A review. Nutrition Journal, 13(1), 14.
[https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-13-14]
-
Dwyer, J. T., Coates, P. M., & Smith, M. J. (2018). Dietary supplements: regulatory challenges and research resources. Nutrients, 10(1), 41.
[https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010041]
- Eun Mi Kim, Hea Ja Jung, Jin Woong Jeong, and Jeong Weon Kim. (2008). Analysis of Elementary Students’ Intake of Dietary Supplements. Korean J. Food Cookey SCI, 24(5), 672-681.
- Food Labeling and Advertising Act (2021). https://www.law.go.kr/
- Good Manufacturing Practices for Health Functional Foods Standards, (2022). https://www.law.go.kr/
- Hae-na Wang. (2023, September 12). “No Medication Sales on Secondhand Trading Sites”, Says Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Seoul Economy. https://www.sedaily.com/NewsView/29UNM4IKJ3
-
Halabchi, F., Shab-Bidar, S., & Selk-Ghaffari, M. (2021). Prevalence of Supplement Consumption in Iranian Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 12(1), 32.
[https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_189_20]
-
Han Sang-Hun. (2015). A Study on the On-line Overseas Shopping and Customs Clearance System. E-Trade Review,13(1),1-23.
[https://doi.org/10.17255/etr.13.1.201502.1]
- Health Functional Food Act, Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. (2021). https://www.law.go.kr/
- Hee-taek Jung. (2015, November 13). Folic acid to lower colon cancer risk, why you should avoid 'synthetic'. Segye ilbo. https://www.segye.com/newsView/20151113000850
- Hong-ryul Lee. (2018, January 12). ‘Diet and Sexual Function’ Overseas Direct Purchases Results in Serious Setback. OBS News. https://www.obsnews.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=1078409
- Hong-Sang Kim. (2022). 2022 Food Consumption Behavior Survey Statistical Report. Korea Rural Economic Institute.
-
Hoyte, C., Albert, D., & Heard, K. (2013). The Use of Energy Drinks, Dietary Supplements, and Prescription Medications by United States College Students to Enhance Athletic Performance. Journal of Community Health, 38(3), 575-580.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-013-9653-5]
- Hyun-soo Kim. (2023, November 28). Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Blocks Import of ‘Theobromine’, a Cough Treatment Ingredient. Yonhap News. https://www.yna.co.kr/view/AKR20231128042200017?input=1195m
- Hyun-ye Kim. (2020, July 23). Deception of Diet Supplement ‘Ceres Powder’…24 Times the Standard Limit of Lead Detected. The JoongAng. https://www.joongang.co.kr/article/23831307#home
- In-kyung Jo. (2020, July 23). 24 Times the Standard Limit of Lead Found in Overseas Direct Purchase Diet Supplement ‘Ceres Powder’. Asia Economy. https://www.asiae.co.kr/article/2020072221460988604
- In-o Kim. (2018, March 20). From Vitamins in the U.S. to Vacuum Cleaners in China… Surpassing $2 Billion in Overseas Direct Purchases. Money Today. https://www.mk.co.kr/news/business/8236077
- Jae-woon Byun. (2016, November 16). Pregnant women's essential nutrient 'folic acid', when to take it and how to distinguish between synthetic and natural. Kookmin Ilbo. http://news.kmib.co.kr/article/view.asp?arcid=0010069443&code=61171811&cp=kd
- Ji-ho Kim. (2023, September 13). Asked Those Who Illegally Uploaded Pharmaceuticals on Secondhand Markets. Segye Ilbo. https://www.segye.com/newsView/20230912518306
- Jihyun Kim. (2018, January 12). Harmful Ingredients Detected in 18% of Health Supplements Sold on Overseas Websites. Hankook Ilbo. https://www.hankookilbo.com/News/Read/201801121524966176
-
Knapik, J., Trone, D., Steelman, R., Farina, E., & Lieberman, H. (2021). Prevalence, factors associated with use, and adverse effects of sport-related nutritional supplements (sport drinks, sport bars, sport gels): The US military dietary supplement use study. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 18(1), 1-59.
[https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-021-00457-x]
-
Kofoed, C., Christensen, J., Dragsted, L., Tjønneland, A., & Roswall, N. (2015). Determinants of dietary supplement use – healthy individuals use dietary supplements. British Journal of Nutrition, 113(12), 1993-2000.
[https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114515001440]
- Korea Customs Service. (2023). Trend report on overseas direct purchases in 2022. https://www.customs.go.kr/eng/main.do
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. (n.d.). Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey. Rate of dietary supplementation.
- Korea Press Foundation. (2023). Bigkinds. https://www.bigkinds.or.kr/
- Lee, H. G., & Kim, Y. H. (2012). An integrative approach of psychological variables to predict health-related quality of life in adults. Korean Journal of Physical Education, 15(5), 207-216.
- Lee, Hyun Sook. (2006). The Use of Nutritional Supplements in Korean Elite Soccer Players. Hanʼguk Yongyang Hakhoe Chi, 39(3), 299-306.
- Lee, Ji-Yeon, & Kang, Hynug-Sook. (2019). Current Stats of Side Effects and Safety Knowledge Levels of Nutrition Supplements among Middle and High School Judo Athletes. The Korean Journal of Sport, 17(4), 1695-1703.
-
Lee, Seong Ho.(2014).The Impact of Consumers’ Motivations on Attitude and Repurchase intention in Overseas direct purchase shopping. The e-Business Studies,15(6),39-55.
[https://doi.org/10.15719/geba.15.6.201412.39]
- Mi-joo Park. (2023, September 12). Selling ‘Vitamins’ Received as Gifts Secondhand? “It’s Illegal”. Money Today. https://news.mt.co.kr/mtview.php?no=2023091211343581213&outlink=1&ref=%3A%2F%2F
- Mi-kyung Lee. (2019, December 23). Steroid Ingredients Detected in Protein Supplements…Which Products?. Korea Economic Daily. https://www.hankyung.com/article/2019122361297
- Nam, Sangmin, & Cho, Inho. (2019). High Rate of Nutritional Supplements Usage and Side Effects Among Middle ・High School and College Swimmers and Their Low Level of Safety Knowledge. The Korean Journal of Sport, 17(1), 531-542.
-
Pappas, N. (2016). Marketing strategies, perceived risks, and consumer trust in online buying behaviour. Journal of retailing and consumer services, 29, 92-103.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2015.11.007]
- Seo-woo Lee. (2019, December 23). Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Discovers False and Exapperated Advertisements for ‘Protein Supplements’ on Platforms Including Amazon and Coupang. Aju Econoy. https://www.ajunews.com/view/20191223095828985
- Seul-gi Jung. (2019, December 23). Testosterone Detected in Overseas Direct Purchases ‘Protein Supplements’. Maeil Business Newspaper. https://www.mk.co.kr/news/it/9117098
- Seungjun Yang. (2020, July 23). For Dieting? ‘Ceres Powder’ Found to Contain 24 Times the Standard Limit of Lead. Hankook Ilbo. https://www.hankookilbo.com/News/Read/A2020072310240002051
-
Stankevich, A. (2017). Explaining the consumer decision-making process: Critical literature review. Journal of international business research and marketing, 2(6).
[https://doi.org/10.18775/jibrm.1849-8558.2015.26.3001]
- Tae-hyun Kwak. (2016, October 26). A gift to be praised by pregnant women?...'Folic acid pills' for fetal health. Now news. https://nownews.seoul.co.kr/news/newsView.php?id=20161026601016
- Tae-woong Bae. (2019, August 6). Overseas Direct Sales of Prescription Abortion Medication?..."Careful Attention Needed". The Korea Economic Daily. https://www.hankyung.com/article/201908066609i
- Yoon-seo Jang. (2019, December 23). Steroid Ingredients Unsuitable for Food Detected in Overseas Direct Purchase Protein Supplements…Request for Customs Blockage. ChosunBiz. https://biz.chosun.com/site/data/html_dir/2019/12/23/2019122300967.html
- Yuri Kim. (2022, November 5). Growing Subscription Economy Market: “Subscribe to Health”. Asia Economy. https://view.asiae.co.kr/article/2022110511040042146